Flax is a food and fiber crop that is traditionally grown in cooler regions of the world, including many states in the USA. It has been part of the global food supply and has been fed to animals for thousands of years. 
Flax (Linum usitatissimum) has long been known to be a natural source of lignans (antioxidants) and omega-3 fatty acids (ALA). Flaxseed and its oil have repeatedly been demonstrated to be non-toxic and are generally recognized as safe (GRAS).
Flax as a Source of hemp
There was an amazing discovery made by European scientists in 2011- flax contains cannabinoids, specifically cannabidiol (hemp), which can be extracted for potential nutraceutical applications. Researchers found that the biological activity of the hemp preparation from flax was the same as the pure compound isolated from C. sativa. (Styrczewska, p.496) “The existence, nature, biosynthesis pathway and activity of cannabinoids in flax requires much further investigation, but the discovered compounds give great new possibilities for flax product applications…”(Czemplik pp. 427-428).
Just as Canna-Pet® innovated the hemp-based cannabinoid industry for pets in 2013, we are now harnessing the phytochemical potential of flax as a nutraceutical.
Learn more about Cannabinoid Phytochemistry
Sources:
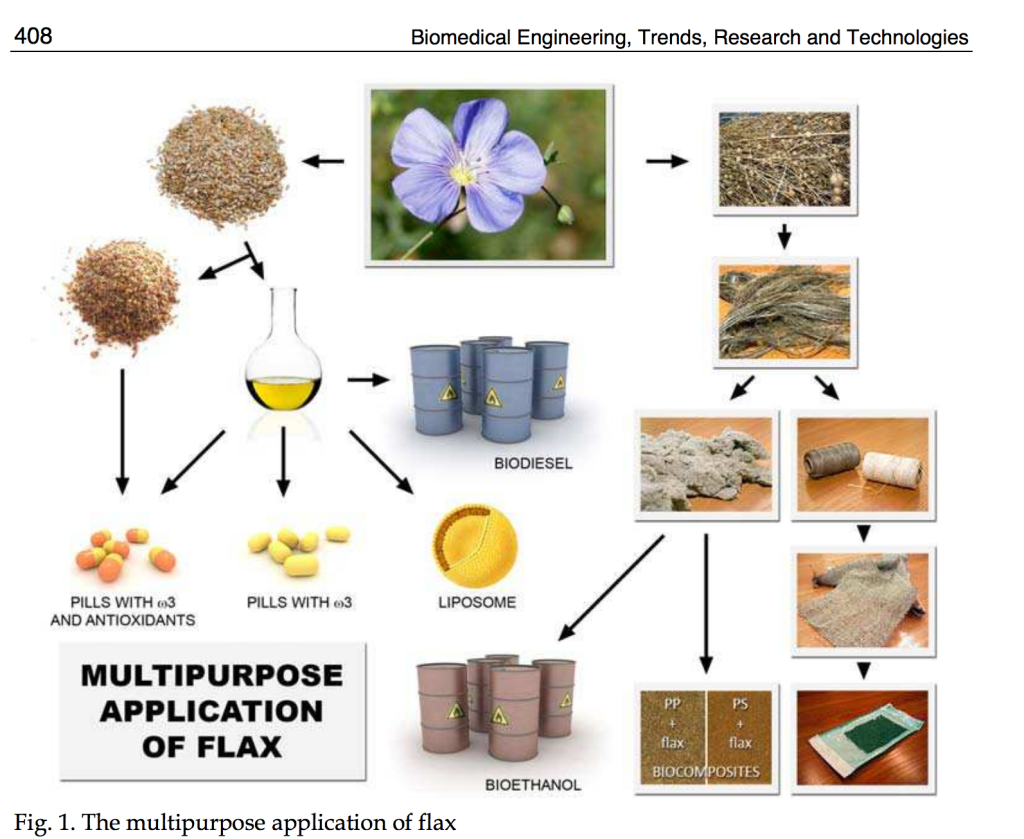
Flax Engineering for Biomedical Application, Magdalena Czemplik, Aleksandra Boba, Kamil Kostyn, Anna Kulma, Agnieszka Mituła, Monika Sztajnert, Magdalena Wróbel- Kwiatkowska, Magdalena Żuk, Jan Szopa and Katarzyna Skórkowska- Telichowska, “Biomedical Engineering, Trends, Research and Technologies”, book edited by Malgorzata Anna Komorowska and Sylwia Olsztynska-Janus, ISBN 978-953-307-514-3, Published: January 8, 2011.
Cannabinoid-like compounds from flax fiber, Monika Styrczewska, Anna Kulma , Katarzyna Ratajczak, Ryszard Amarowicz, Jan Szopa, Cellular and Molecular Biology Letters, September 2012, Copyright © 2012 Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters Journal.